Introduction to LOINC¶
LOINC stands for Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC). According to Regensrief, who developed and maintains LOINC:
The LOINC website provides a very detailed explaination of LOINC. Here, we try to briefly illustrate the essence of LOINC and focus on the aspects that are relevant to this app.
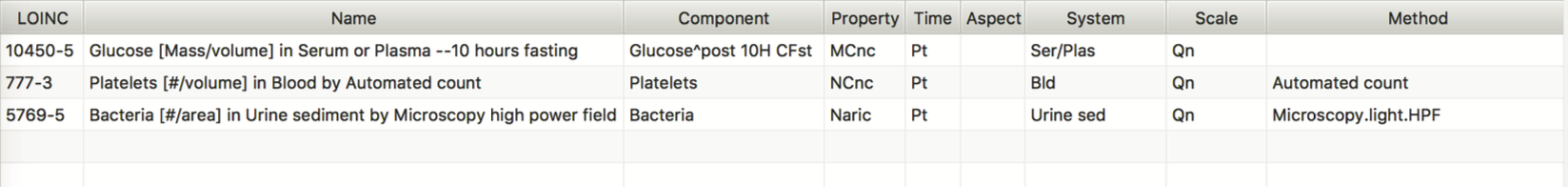
In essence, LOINC is simply a big table with ~86,000 entries that define the names and IDs of laboratory tests. The following shows three examples of LOINC codes:
You can see that each LOINC entry simply represents a laboratory test. The first column LOINC contains a value with at most 7 numbers, separated by a -. This number is unique so that using it can uniquely identify an laboratory test. For example, 10450-5 represents a glucose test called “Glucose [Mass/volume] in Serum or Plasma”, while 777-3` represents a test on the count of platelets “Plates [#/volume] in Blood by Automated count”. Each LOINC entry have several other fields that define the test from different aspects.
Parts of LOINC entry¶
Component: defines the analyte in the test
Property: defines “kinds of quantities”. It can be divided into five several categories, mass, substance, catalytic activity, and number or counts. Each category is further divided into subclasses, for example MCnc or “mass concentration” is a subclass of “mass” property, while NCnc or “number of concentration (count/vol)” and Naric or “number aeric (number per area)” are subclasses of counts.
Time: defines whether a measurement was made at a moment, or aggregated from a series of physiologic states. The three examples are all PT (“points”), meaning that they are measurements at a single time point. As an example, a test on “daily urine amount” will be labeled as 24H (“24 hours”).
Aspect: defines a modifier for a measurement over a duration. For example, “8H^max heart rate” means the “max” heart rate measured during an 8-hour period. Min, max, first, last, mean typically appear here.
System: can be considered as the specimen for the test, such as “serum”, “blood”, “urine”, “cerebrospinal fluid” etc.
Scale” defines the scale of the measurement. Scale is the most important information for our application. The following table summarizes possible values of scale.
Table 12: Type of Scale (ref1)
| Scale Type | Abbr. | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative | Qn | The result of the test is a numeric value that relates to a continuous numeric scale. Reported either as an integer, a ratio, a real number, or a range. The test result value may optionally contain a relational operator from the set {<=, <, >, >=}. Valid values for a quantitative test are of the form “7”, “-7”, “7.4”, “-7.4”, “7.8912”, “0.125”, “<10”, “<10.15”, “>12000”, 1-10, 1:256 |
| Ordinal | Ord | Ordered categorical responses, e.g., 1+, 2+, 3+; positive, negative; reactive, indeterminate, nonreactive. (Previously named SQ) |
| Quantitative or Ordinal | OrdQn | Test can be reported as either Ord or Qn, e.g., an antimicrobial susceptibility that canbe reported as resistant, intermediate, susceptible or as the mm diameter of the inhibition zone. (Previously named SQN) We discourage the use of OrdQn in other circumstances. |
| Nominal | Nom | Nominal or categorical responses that do not have a natural ordering. (e.g., names of bacteria, reported as answers, categories of appearance that do not have a naturalordering, such as, yellow, clear, bloody. (Previously named QL |
| Narrative | Nar | Text narrative, such as the description of a microscopic part of a surgical papule test. |
| “Multi” | Multi | Many separate results structured as one text “glob”, and reported as one observation, with or without imbedded display formatting. |
| Document | Doc | A document that could be in many formats (XML, narrative, etc.) |
| Set | Set | Used for clinical attachments |
ref1: LOINC USERS’ GUIDE, P32
Qn, Ord and Nom are the three most frequently used LOINC in real world, accounting for probably 99% cases, particularly Qn, which may account for 80% cases alone. Qn values may be continuous (e.g. serum sodium concentration) or discrete (e.g. titers, 1:16, 1:32). The most frequent Ord type are “yes/no” tests (e.g. presence or absence of a substance in the blood).
Aside from the three main types, Nar are reported as free texts.
Method: defines the method used for the measurement.